If a router of INSYS icom is running an OpenVPN-Server, it is possible to establish OpenVPN connections to this from a computer.
Situation
A Windows computer shall be included as a client into an existing OpenVPN network on an INSYS router.
Solution
The OpenVPN package will be installed on the computer. The configuration file will be generated using the OpenVPN server configuration of the INSYS router on the computer. Instructions for configuring an OpenVPN server on an INSYS router can be found in the respective Configuration Guide.
It is prerequisite that the respective certificates and keys are available and the configuration of the server is known.
Installing the OpenVPN package on the computer
-
Download the latest OpenVPN package for your computer under https://openvpn.net/community-downloads/. [1]
-
Open the installation file and perform the installation according to the instructions.
The OpenVPN package will be installed on your computer in the default directory C:Program Files\OpenVPN.
Storing the certificates and keys on the computer
-
Copy the CA certificate, the client certificate and the client key to the directory C:Program Files\OpenVPNconfig on the computer. These can also be contained in an PKCS#12 container.
Creating and configuring the OpenVPN configuration file on the computer
-
Download the OpenVPN client template and edit it in a text editor or copy the content from the window below and insert it into a text editor.
-
Adapt the content of the template according to the comments behind the parameters and save it under a suitable name.
-
Copy the file into the directory C:Program Files\OpenVPNconfig of the OpenVPN installation.
client # configures the OpenVPN terminal as client and activates tls-auth and pull remote 192.168.1.1 # <192.168.1.1> replace with IP address or domain name of the router with the OpenVPN server (1) ca ca.crt # <ca.crt> replace with file name of the certificate of the Certification Authority (CA) key client1.key # <client1.key> replace with file name of the private client key cert client1.crt # <client1.crt> replace with file name of the client certificate proto udp # <udp> replace with tcp, if the TCP protocol is used by the server (2) rport 1194 # <1194> replace with the port, which is configured on the server for the remote tunnel end (3) lport 1194 # <1194> replace with the port, which is configured on the server for the local tunnel end (4) comp-lzo # activates LZO compression; delete, if this is not enabled on the server (5) dev tun # configures the virtual network interface TUN for routing
| 1 | See Determining the IP address of the OpenVPN server accessible from the Internet below |
| 2 | Configured in the web Interface: of the router on the Interfaces → OpenVPN page for the respective OpenVPN interface under Protocol |
| 3 | Configured in the web Interface: of the router on the Interfaces → OpenVPN page for the respective OpenVPN interface under Tunnelling over port (remote) |
| 4 | Configured in the web Interface: of the router on the Interfaces → OpenVPN page for the respective OpenVPN interface under Tunnelling over port (local) |
| 5 | Configured in the web Interface: of the router on the Interfaces → OpenVPN page for the respective OpenVPN interface under Activate LZO compression |
If all certificates are contained in a PKCS#12 container, delete the three lines for the certificates and the key and insert the line pkcs12 client1.p12.
Then, replace <client1.p12> with the file name of the PKCS#12 container.
|
Determining the IP address of the OpenVPN server accessible from the Internet
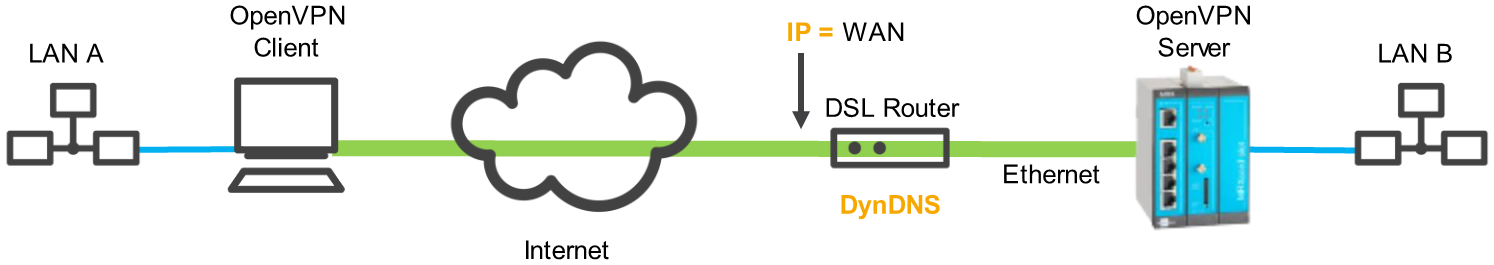
The IP address that is accessible from the Internet depends on the architecture of the router network. If the router is behind a DSL router like in the following figure for example, its WAN IP address must be used. A corresponding port forwarding rule of the tunnel to the router must be present in the DSL router.
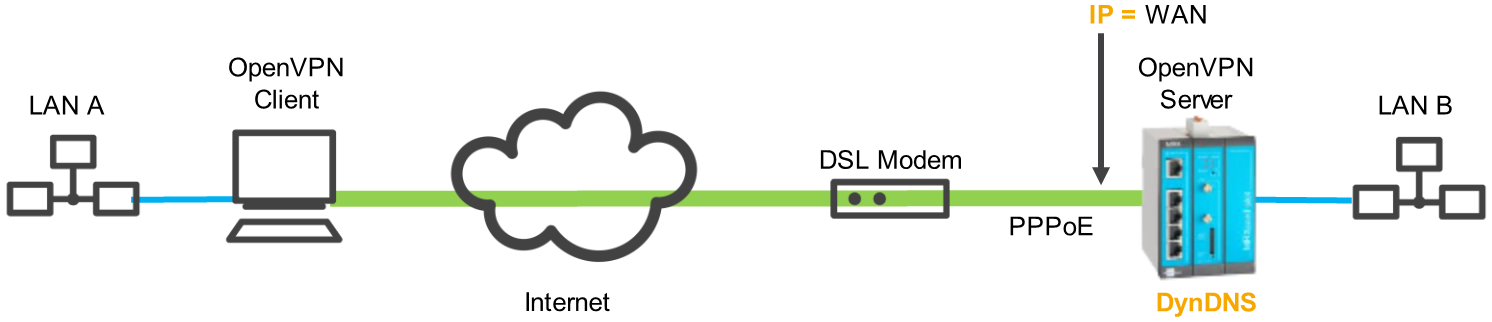
If the router is directly connected to a DSL modem without intermediate router like in the following figure, the IP address of the router must be used.
If the router has no fixed IP address, a DynDNS domain name can also be entered, which will then be resolved by the client. For this, DynDNS must be enabled in the DSL router (first example) or in the INSYS router (second example). Notes regarding this are available in the inline and online help of the INSYS router. A DNS server must also be entered in the client for this.
Staring the OpenVPN client
-
Start the OpenVPN GUI using the Windows key () → OpenVPN → Open-VPN GUI or a click on the desktop icon.
-
Click on the symbol for showing the hidden symbols in the task bar ().
-
Right-click on the symbol of the OpenVPN GUI and click on Connect (or <Name der Konfigurationsdatei> → Connect if several configuration files are available).
-
If the client certificate has been provided with a password, enter this password when prompted.
Result testing
The symbol of the OpenVPN GUI is displayed green as soon as the connection to the OpenVPN server has been established successfully. If the symbol remains yellow, the OpenVPN client tries to reach the server, but the connection cannot be established. A connection log can be displayed using the menu item View Log (or <Name der Konfigurationsdatei> → View Log if several configuration files are available).
Troubleshooting
-
If the OpenVPN GUI does not find the configuration file in the directory, it may have happened that a text editor has appended the file extension .txt accidentally.
Back to the Configuration Guides for icom OS Smart Devices
Back to overview