 |
Online help |
Netfilters
The netfilters in the router manipulate and block all data packets on their way from the sender interface to the destination interface as shown in the following sketch. The netfilters consist of NAT (Network Address Translation) and IP filter (Firewall) rules.
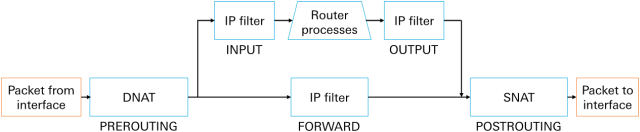
All data packets arriving at the interface pass through all destination NAT (DNAT) rules of the table PREROUTING in sequence and will then be manipulated and forwarded accordingly when the first rule applies.
All data packets not directed to the router run through the rules of the Filter table of the FORWARD chain and will be allowed to pass (are permitted to pass the firewall) as soon as a rule applies. This is the case for example, if a locally connected device sends data to the Internet.
All data packets directed to the router run through the rules of the Filter table of the INPUT chain and will be allowed to pass (are permitted to pass the firewall) to the router as soon as a rule applies. This is the case for example, if the web interface of the router is accessed or the DHCP or VPN server of the router is contacted.
All data packets generated by the router run through the rules of the Filter table of the OUTPUT chain and will be allowed to pass (are permitted to pass the firewall) as soon as a rule applies. This is the case for example, if the router makes NTP or DNS requests or initiates a tunnel.
All data packets which leave the chains OUTPUT and FORWARD, pass through all source NAT (SNAT) rules of the table POSTROUTING in sequence and will then be manipulated and forwarded to the interface accordingly when the first rule applies.
The netfilter rules defined in the router can be displayed in the Status menu on the iptables page.
Example for a NAT rule for port forwarding
Examples for typical IP filter (Firewall) rules